


|

|
About Frogs |
 |
Evolution Imagine traveling back through time millions of years to the age of the dinosaurs. Pterodactyls glide above a soggy marsh. Nearby, a colossal 80-ton Brachiosaurus munches on a tree. On the ground at its feet, something strangely familiar hops by... a frog. |
 |
Symbols of Fertility
|
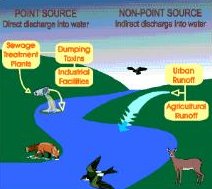 |
Bio-indicators The health of frogs indicates the health of the ecosystem. |
 |
Mouths Frogs eat live prey, insects, snails, worms, small fish. A tongue strike requires less than 1 second. |
 |
Eyes Frogs have keen eyesight to locate prey. They see colors and in dim light. Their bulging eyes see in all directions. |
 |
Legs Frogs can leap up to twenty times their body length, which is the same as 100 feet for a human. |
 |
Skin Frogs get moisture through their skin. They
|
 |
Calls Males call during mating. The calls can carry up to 1 mile. Female ears are "tuned" to species call. |
 |
True Frogs (Ranids) Bullfrog Green Frog Wood Frog S. Leopard Frog Pickerel Frog |
 |
Tree Frogs (Hylids) Spring Peeper Striped Chorus Frog Gray Treefrog Green Treefrog Northern Cricket Frog |
 |
Toads (Bufids) American Toad Fowler's Toad Spadefoot Toad |